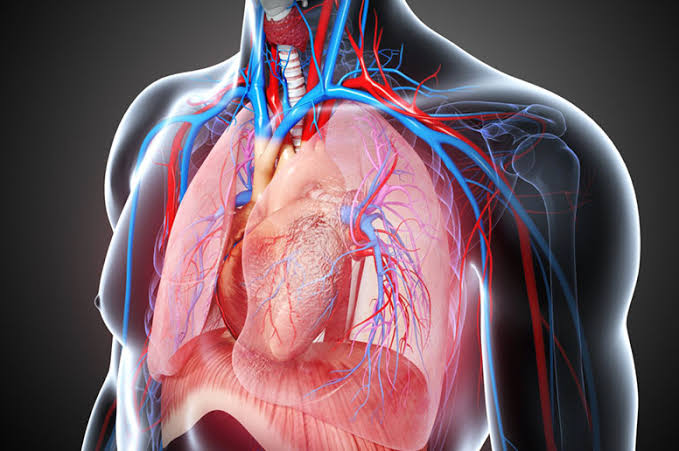
Angina (Chest Pain):
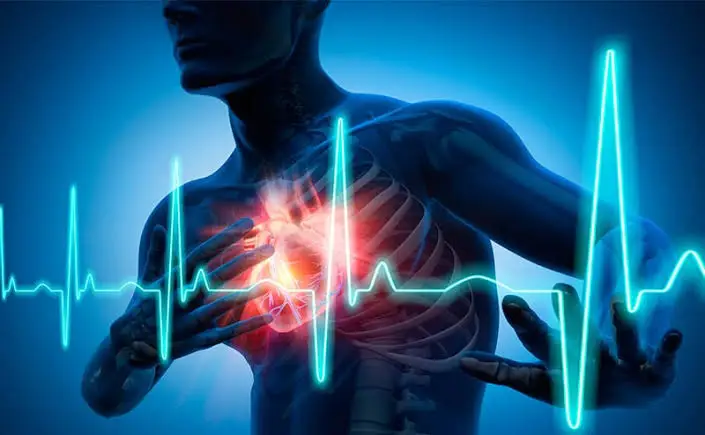

In general, ECP therapy is considered for patients with heart disease, particularly when other options (like medications or surgery) have failed or are not suitable. Its benefits for improving circulation and heart function are significant, especially for patients with chronic and refractory conditions.
© Copyright 2024. Designed & Developed by Fine World Innovations.
WhatsApp us